Electronic Batch Records for Smart Manufacturing
- An Overview of Master Electronic Batch Records
- Benefits of Electronic Batch Record Systems
- Title 21 CFR Part 11 & Data Integrity
- What Goes Into an Electronic Batch Record EBR System?
- Popular Trends of EBRs
- MES Software Implementation Methods
- What Other Software is Needed to go Digital?
Life Science manufacturers that grapple with maintaining FDA compliance by paper-based batch records are finding out of control manual errors and lack of enforcement are a perfect storm for product recall. Today’s regulated industries are getting smart by making a move from paper-driven manufacturing plants to modern digital smart factories by implementing electronic batch records software. POMSnet Aquila Manufacturing Execution Software solution has been a long-established industry choice in digital transformation for pharma and biotech companies to go beyond GMP compliance.
What is a Production Batch Record?
Life science manufacturers in Pharmaceutical, Biotech, or Cell & Gene therapies and many other industries are required to follow Good Manufacturing Practices GMP and FDA requirements during the manufacturing process of medicinal products or therapies. The batch record is a product quality controlled document that collects all the data and information to make a regulated product. Batch records record materials, equipment, people, data, labels, and events during the production of products. In autologous cell and gene therapy manufacturing, a single patient's cells are engineered to fight diseases, like cancer or genetic disorders, the entire batch record is devoted to just one patient's data.
Odkryj emocjonującą grę w plinko casino i ciesz się wyjątkowymi możliwościami wygranej w Polsce.
Quality personnel use the batch record process to review the manufacturing process had followed standard operating procedures SOP’s, critical quality attributes CQA’s, and critical process parameters CPP’s. In some cases, the controlled document is used for investigating deviations or exceptions that occurred during the production. The severity of these events can potentially cause rework or even a complete loss of a drug substance or therapy.
Entdecken Sie die besten sweet bonanza erfahrungen bei unserem Partnercasino in der Schweiz und genießen Sie spannende Spielrunden.
Benefits of Electronic Batch Records
Delivering Right the First-Time mentality is a quality mindset companies aspire to, but only a few achieve. Quality goes beyond checkmarks and rubber stamps. Manufacturing execution systems like POMSnet Aquila MES enable best practices and a culture of quality enterprise-wide. Everyone in the organization follows the production and quality procedures. Digital workflows and electronic batch records ensure operators and staff follow the quality mindset and best practices of pharmaceutical manufacturing.
- Reduce Cycle Times
- Data Access
- Digital Transformation
- Real Time Visibility
Regulations of Batch Records and Electronic Signatures and Records
The health sciences industry is a government-regulated industry that ensures companies that use electronic batch record software are in the highest levels of compliance. Pharma and biotech companies follow agency recommended guidelines called Good Manufacturing Practices or cGMP. The purpose of these minimum requirements is to make sure drug products are safe for use, that the ingredients and strength of claims are accurate, and the FDA can oversee public health.
Naši partneři nabízejí plinko hra v České republice, více informací naleznete na stránce plinko hra.

FDA Title 21 CFR Part 11
Title 21 Code of Federal Regulation Part 11 defines the criteria under which electronic records and electronic signatures are considered trustworthy, reliable, and equivalent to paper records. Having a software company with 30 years of experience in life science is essential to know how to quickly and effectively implement software first time right.
FDA Data Integrity
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration has created draft guidance on data integrity for the pharmaceutical (including biologics) manufacturers required to adhere to the U.S. Code of Federal Regulations 21 CFR Parts 210–212. There have been increasing issues related to data integrity in the industry, and these data integrity-related cGMP violations have led to numerous regulatory actions, including warning letters, import alerts, and consent decrees.
Good Manufacturing Practices cGMP
Are the practices required in order to conform to the guidelines recommended by agencies that control the authorization and licensing of the manufacture and sale of food and beverages,[1] cosmetics,[2] pharmaceutical products,[3] dietary supplements,[4] and medical devices.[5] These guidelines provide minimum requirements that a manufacturer must meet to assure that their products are consistently high in quality, from batch to batch, for their intended use.
Erleben Sie das aufregende plinko ch und tauchen Sie ein in das beste Casino-Spiel in der Schweiz.
Good Automated Manufacturing Practices GAMP5
GAMP® 5 provides pragmatic and practical industry guidance to achieve compliant computerized systems fit for intended use in an efficient and effective manner. This technical document describes a flexible risk-based approach to compliant GxP regulated computerized systems, based on scalable specification and verification. It points to the future of computer systems compliance by centering on principles behind major industry developments such as PQLI; ICH Q8, Q9, Q10, and ASTM E2500.
Naši partneri ponúkajú Plinko casino game na Slovensku, kde si môžete prečítať podrobné plinko recenze na stránke.
What Information Goes into an Electronic Batch Record and What Does an Example EBR Look Like?
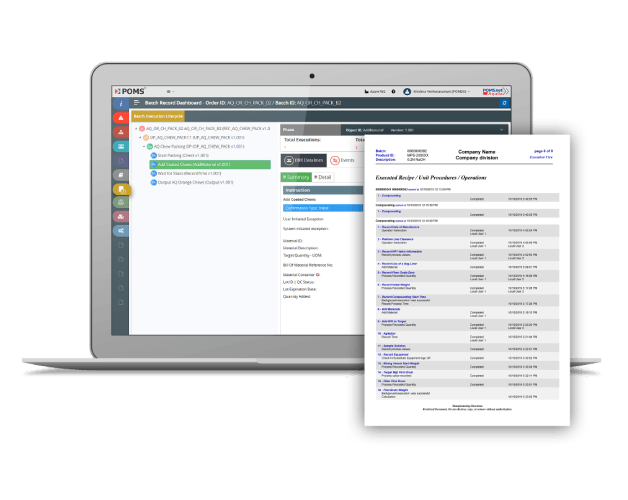
- Header
- Table of Contents
- Exception Summary
- Equipment Usage Summary
- Material Usage Summary
- Actual Batch Record Details
- Representations of Product Labels
- User Exits
- Any Scanned Paper Forms Attached
The details of an EBR can vary from one company to the next. Pharma and Biotech companies may want to print a PDF of the electronic batch records for an agency inspector rather than grant a login to the software. Cell Therapy companies may only want a dashboard of the exceptions in the process to release a patient’s therapy in real-time. RD Engineers may only be interested in a subset of the record to query the database for specific in-process test results.
Formats between PDFs, dashboards, or tables can also have a role in defining an EBR. Examples could be a private link in an email to an HTLM5 webpage given to a client to review in real-time the production process from a remote location. There is no one size fits all when it comes to what an Electronic Batch Record example looks like; more importantly, is how your organization will consume the digital data available to everyone now.
Popular Trends to use EBR Software to Drive Operational Excellence?
Digital workflows enforce product safety and specifications while guiding trained clerks, operators, and engineers to follow best practice operational steps. New manufacturing models like Cell and Gene therapy are capturing patient’s medial information along with equipment, materials, and calculated data during production. Important operational information like events, alarms, exceptions, and deviations are evoked and responded to by EBR software and notifications in real-time for actions. Many mature companies will implement continuous improvement plans or best practices into the recipe operations. One example would be adding equipment cleaning expiry. The most popular trends for using EBR software are:
-
Review-by-exception
- a validated process for quality staff to review only the deviations data that occurred in a batch and once all exceptions are addressed the batch is released. Unlike paper systems in which the entire data record is reviewed even if passing.
-
Quality Metrics KPIs
- modern manufacturing includes robust quality metrics programs as a foundation for continual improvement of product and process quality. Quality metrics are one element of companies’ commitment to a quality culture.
Kumppanimme Plinko-kasinopeli Suomessa tarjoaa hauskan ja palkitsevan pelikokemuksen, jonka löydät plinko game -sivustolta plinko game.
-
Audit Ready
- companies with a cloud-based MES, or Software as a Service SaaS model, can rest assured IT infrastructure is reliable. Companies can rely on partners like Validated Cloud to be FDA audit-ready for IT infrastructure.
-
MES Centers of Excellence
- The best way to maintain a competitive advantage is to build an MES Center of Excellence CoE organization. Bringing together a cross-functional team with shared resources and tools, like MES, is the best way a company can achieve the highest levels of operational agility.
How do Companies Implement EBR Workflows?
There are many variables a company needs to consider when determining an implementation strategy. GAMP5 ISPE guidebooks recommend two methods; Horizontal strategies or Vertical strategies for MES implementation.
The vertical method implements the MES core unit operation across multiple sites before proceeding to the next operation step. An example of this is Material Management as a first project phase, then Weigh and Dispense as a next project phase and repeat this process until all manufacturing operations are covered. The Vertical MES Strategy method allows for centers of excellence CoE’s competency to practice implementing the same MES functionality.
In contrast to Vertical, the Horizontal MES strategy implements a single MES product recipe end-to-end solution across multiple unit operations. It then repeats recipe authoring one product at a time and on-boards new products over time. The Horizontal MES strategy lets companies reap benefits quicker, but projects can be more complicated because of more complex recipe authoring.
Companies have unique challenges that paperless operation aims to solve. Autologous Cell Therapy companies are looking to return single patient CAR-T therapies as fast as possible and may consider a review-by-exception as a phase one project. Other business models like Contract Development and Manufacturing Organizations CDMO’s may prioritize material management and inventory controls over an EBR to accurately manage client materials before production to avoid mishandling and quarantines.
What Other Software is Needed for Batch Records to go Digital?
To make a move from paper to digital electronic batch records, you will need a blueprint of the following software ecosystems in a typical manufacturing organization and how these systems will work together. Contact POMS Professional Services and Consulting group to help you make a move to digital.
Software systems across your pharmaceutical manufacturing supply chain like enterprise resource planning ERP or laboratory information management systems LIMS are usually early systems to implement. SAP and Oracle are the more popular ERPs in place though you don’t necessarily need to have either.
Next, you will need to think about how the software will communicate to devices, instruments, and hardware data that you will want to capture automatically. Popular and flexible communication is commonly used by OPC protocol, which allows many automation brands to communicate over a single standard communication. Other software for communicating between databases employ Web APIs or Web Services to facilitate seamless integration. Be sure to ask your other vendors about their Web API’s tools or Web Services when choosing software packages for future proof integrations.
For companies with limited on-site IT expertise or lacking the real estate footprint for hosting physical servers, they can consider POMSnet Aquila cloud-based MES with a Software as a Service SaaS model. This flexible option can help your company with costly overhead for database administrators while enjoying reliable 99% high availability and private VPN security. Cloud-based MES is becoming a popular demand for new startup companies with their main priority in clinical operations without having to commit and invest during pre-commercial operations.
POMSnet Aquila MES is the Popular Choice for Pharma, Biotech, and Cell Therapy Software to Meet Regulated Compliance and Electronic Batch Records
Start your Digital Operations Here

